Week 11
Week 11: Tuesday, January 9, 2024
What Kind of Revolution?
WEEK 11
What Kind of a Revolution Did We get?
Gordon Wood: "Americans were not born free and democratic in any modern sense; they became so—and largely as a consequence of the American Revolution. After eighteenth-century Americans threw off their monarchical allegiance in 1776, they struggled to find new attachments befitting a republican people. Living in a society that was already diverse and pluralistic, Americans realized that these attachments could not be the traditional ethnic, religious, and tribal loyalties of the Old World. Instead, they sought new enlightened connections to hold their new popular societies together. But when these proved too idealistic and visionary, they eventually found new democratic adhesives in the actual behavior of plain ordinary people—in the everyday desire for the freedom to make money and pursue happiness in the here and now. To base a society on the commonplace behavior of ordinary people may be obvious and understandable to us today, but it was momentously radical in the long sweep of world history up to that time. This book attempts to explain this momentous radicalism of the American Revolution."
Gordon Wood, The Radicalism of the American Revolution (p. 2). Knopf Doubleday Publishing Group.
RECOMMENDED READING

Gordon S. Wood,
The Radicalism of the American Revolution,
Vintage; Reprint edition (March 2, 1993),
ISBN 978-0679736882
REQUIRED READING FOR THE WHOLE YEAR OF HISTORY OF THE USA
Wilfred McClay, Land of Hope:
"There were unsettling questions for the Americans about the revolutionary journey on which they found themselves embarked. What sort of effect was this war having on the social and political life of the colonies-becoming-a-nation? How was it changing things? If this was to be a revolution, how thoroughgoing a revolution was it to be? Was, in fact, the world being turned upside down – or merely right side up? The latter might have seemed more likely. As we’ve seen, the most influential justifications offered in favor of revolution invoked not radical change but rather restoration – restoring and protecting the colonists’ customary rights as Englishmen – as the pretext for revolution. But like any great historical event, the American Revolution was complicated, with many aspects. Even those fighting on the same side sometimes saw the cause differently. To a greater extent than many of us appreciate today, the Revolutionary War took on many of the aspects of a civil war, pitting Loyalists against Patriots; dividing families, towns, regions, and social classes; and producing fierce struggles over fundamental political and social values.values. Loyalty to the Crown had been the instinctive response of a sizable minority of Americans. But for some, the resonant words of the Declaration of Independence pointed toward a larger aspiration, something more than mere restoration. Such an interpretation pointed toward the emergence on the world stage of something genuinely new: a republican order built upon a principled commitment to both equality and liberty. Historians have been arguing for generations which of these different tendencies was dominant and hence which offers us the best way to think about the Revolution. Was the Revolution essentially conservative in its objectives, merely seeking to separate America from Britain to return the political order to what it had been before the disruptions caused by clumsy and wrongheaded British colonial policies? Or was it something radical, in the sense of wishing to shake things up, dramatically and fundamentally upending the entrenched inequalities and hierarchies in society, and not merely changing the names and faces of those at the top of the political structure? As the American historian Carl Becker, who strongly advocated for the latter view, put it memorably more than a hundred years ago, “the war was not about home rule, but about who would rule at home.”
McClay, Wilfred M.. Land of Hope (pp. 58-59). Encounter Books.
RECOMMENDED READING

Gordon Wood,
Empire of Liberty,
Oxford University Press; 1st edition (October 28, 2009),
ISBN 978-0195039146
12
Week 12: Tuesday, January 16, 2024
Writing the Constitution
WEEK 12
The Constitution of the United States is the supreme law of the United States of America. It superseded the Articles of Confederation, the nation's first constitution, in 1789. Originally comprising seven articles, it delineates the national frame and constraints of government. The Constitution's first three articles embody the doctrine of the separation of powers, whereby the federal government is divided into three branches: the legislative, consisting of the bicameral Congress (Article I); the executive, consisting of the president and subordinate officers (Article II); and the judicial, consisting of the Supreme Court and other federal courts (Article III). Article IV, Article V, and Article VI embody concepts of federalism, describing the rights and responsibilities of state governments, the states in relationship to the federal government, and the shared process of constitutional amendment. Article VII establishes the procedure subsequently used by the 13 states to ratify it. The Constitution of the United States is the oldest and longest-standing written and codified national constitution in force in the world today. The drafting of the Constitution, often referred to as its framing, was completed at the Constitutional Convention, which assembled at Independence Hall in Philadelphia between May 25 and September 17, 1787. Delegates to the convention were chosen by the state legislatures of 12 of the 13 original states; Rhode Island refused to send delegates. The convention's initial mandate was limited to amending the Articles of Confederation, which had proven highly ineffective in meeting the young nation's needs. Almost immediately, however, delegates began considering measures to replace the Articles. The first proposal discussed, introduced by delegates from Virginia, called for a bicameral (two-house) Congress that was to be elected on a proportional basis based on state population, an elected chief executive, and an appointed judicial branch. An alternative to the Virginia Plan, known as the New Jersey Plan, also called for an elected executive but retained the legislative structure created by the Articles, a unicameral Congress where all states had one vote. On June 19, 1787, delegates rejected the New Jersey Plan with three states voting in favor, seven against, and one divided. The plan's defeat led to a series of compromises centering primarily on two issues: slavery and proportional representation. The first of these pitted Northern states, where slavery was slowly being abolished, against Southern states, whose agricultural economies depended on slave labor. The issue of proportional representation was of similar concern to less populous states, which under the Articles had the same power as larger states. To satisfy interests in the South, particularly in Georgia and South Carolina, the delegates agreed to protect the slave trade, that is, the importation of slaves, for 20 years. Slavery was protected further by allowing states to count three-fifths of their slaves as part of their populations, for the purpose of representation in the federal government, and by requiring the return of escaped slaves to their owners, even if captured in states where slavery had been abolished. Finally, the delegates adopted the Connecticut Compromise, which proposed a Congress with proportional representation in the lower house and equal representation in the upper house (the Senate) giving each state two senators. While these compromises held the Union together and aided the Constitution's ratification, slavery continued for six more decades and the less populous states continue to have disproportional representation in the U.S. Senate and Electoral College.(Wikipedia)
RECOMMENDED READING

Carol Berkin,
A Brilliant Solution: Inventing the American Constitution,
Harcourt; First Edition (September 13, 2002),
ISBN 978-0151009480
Historian Carol Berkin's A Brilliant Solution: Inventing the American Constitution is a rich narrative portrait of post-revolutionary America and the men who shaped its political future.
"Just as the Constitution was a brilliant solution to the problems of the 1780s, Carol Berkin's book is a brilliant account of the making of that constitution. Written with great verve and clarity, it nicely captures all the contingency and unpredictability in the framing of the Constitution."—Pulitzer Prize-winning author Gordon S. Wood
Though the American Revolution is widely recognized as our nation's founding story, the years immediately following the war — when our government was a disaster and the country was in a terrible crisis — were in fact the most crucial in establishing the country's independence. The group of men who traveled to Philadelphia in the summer of 1787 had no idea what kind of history their meeting would make. But all their ideas, arguments, and compromises — from the creation of the Constitution itself, article by article, to the insistence that it remain a living, evolving document — laid the foundation for a government that has surpassed the founders' greatest hopes. Revisiting all the original historical documents of the period and drawing from her deep knowledge of eighteenth-century politics, Carol Berkin opens up the hearts and minds of America's founders, revealing the issues they faced, the times they lived in, and their humble expectations of success.Note: The new hardcovers available from Amazon, offer a much better price for value than the paperback edition.
RECOMMENDED READING
From the Publisher: "New York Times bestseller and Pulitzer Prize-winning author Gordon S. Wood elucidates the debates over the founding documents of the United States.
The half century extending from the imperial crisis between Britain and its colonies in the 1760s to the early decades of the new republic of the United States was the greatest and most creative era of constitutionalism in American history, and perhaps in the world. During these decades, Americans explored and debated all aspects of politics and constitutionalism--the nature of power, liberty, representation, rights, the division of authority between different spheres of government, sovereignty, judicial authority, and written constitutions. The results of these issues produced institutions that have lasted for over two centuries. In this new book, eminent historian Gordon S. Wood distills a lifetime of work on constitutional innovations during the Revolutionary era. In concise form, he illuminates critical events in the nation's founding, ranging from the imperial debate that led to the Declaration of Independence to the revolutionary state constitution making in 1776 and the creation of the Federal Constitution in 1787. Among other topics, he discusses slavery and constitutionalism, the emergence of the judiciary as one of the major tripartite institutions of government, the demarcation between public and private, and the formation of states' rights. Here is an immensely readable synthesis of the key era in the making of the history of the United States, presenting timely insights on the Constitution and the nation's foundational legal and political documents"
REVIEWS
"No one has done more to teach us about the origins of American constitutionalism than Gordon S. Wood. Now, at a moment when we are trembling over the strength of our constitutional system, Wood gives us a deft shorthand account of how it all began. For anyone who wants to understand what made American constitutionalism such a vital political experiment, this is the place to start." -- Jack Rakove, author of Beyond Belief, Beyond Conscience: The Radical Significance of the Free Exercise of Religion
"Gordon Wood has packed a lifetime of learning into this splendid little volume. In his capable hands, our founding charters, grown stale from familiarity, regain their freshness and allure as revolutionary documents that redefined our politics. Wood has an uncanny ability to project himself into the past and to report on his findings as if he had been a personal witness to those distant events." -- Ron Chernow, author of Alexander Hamilton
"Masterful... No historian knows more about the founding years of the U.S. than Wood. In his latest, he once again demonstrates his characteristic clarity... A fresh, lucid distillation of Wood's vast learning about the origins of American government." --Kirkus, Starred Review
"No living historian has done more to illuminate the origins of our constitutional heritage in the Revolutionary era."--National Review
REQUIRED READING FOR THE WHOLE YEAR OF HISTORY OF THE USA
From the Publisher:
"For too long we’ve lacked a compact, inexpensive, authoritative, and compulsively readable book that offers American readers a clear, informative, and inspiring narrative account of their country. Such a fresh retelling of the American story is especially needed today, to shape and deepen young Americans’ sense of the land they inhabit, help them to understand its roots and share in its memories, all the while equipping them for the privileges and responsibilities of citizenship in American society. The existing texts simply fail to tell that story with energy and conviction. Too often they reflect a fragmented outlook that fails to convey to American readers the grand trajectory of their own history. A great nation needs and deserves a great and coherent narrative, as an expression of its own self-understanding and its aspirations; and it needs to be able to convey that narrative effectively. Of course, it goes without saying that such a narrative cannot be a fairy tale of the past. It will not be convincing if it is not truthful. But as Land of Hope brilliantly shows, there is no contradiction between a truthful account of the American past and an inspiring one. Readers of Land of Hope will find both in its pages."
REVIEWS
“At a time of severe partisanship that has infected many accounts of our nation’s past, this brilliant new history, Land of Hope, written in lucid and often lyrical prose, is much needed. It is accurate, honest, and free of the unhistorical condescension so often paid to the people of America’s past. This generous but not uncritical story of our nation’s history ought to be read by every American. It explains and justifies the right kind of patriotism.”― Gordon S. Wood, author of Friends Divided: John Adams and Thomas Jefferson
“We’ve long needed a readable text that truly tells the American story, neither hiding the serious injustices in our history nor soft-pedaling our nation’s extraordinary achievements. Such a text cannot be a mere compilation of facts, and it certainly could not be written by someone lacking a deep understanding and appreciation of America’s constitutional ideals and institutions. Bringing his impressive skills as a political theorist, historian, and writer to bear, Wilfred McClay has supplied the need.”― Robert P. George, McCormick Professor of Jurisprudence, Princeton University
“No one has told the story of America with greater balance or better prose than Wilfred McClay. Land of Hope is a history book that you will not be able to put down. From the moment that ‘natives’ first crossed here over the Bering Strait, to the founding of America’s great experiment in republican government, to the horror and triumph of the Civil War...McClay’s account will capture your attention while offering an unforgettable education.”― James W. Ceaser, Professor of Politics, University of Virginia
13
Week 13: Tuesday, January 23, 2024
Ratifying the Constitution
WEEK 13
Within three days of its signing on September 17, 1787, the Constitution was submitted to the Congress of the Confederation, then sitting in New York City, the nation's temporary capital.The document, originally intended as a revision of the Articles of Confederation, instead introduced a completely new form of government. While members of Congress had the power to reject it, they voted unanimously on September 28 to forward the proposal to the thirteen states for their ratification. Under the process outlined in Article VII of the proposed Constitution, the state legislatures were tasked with organizing "Federal Conventions" to ratify the document. This process ignored the amendment provision of the Articles of Confederation which required unanimous approval of all the states. Instead, Article VII called for ratification by just nine of the 13 states—a two-thirds majority. Two factions soon emerged, one supporting the Constitution, the Federalists, and the other opposing it, the so-called Anti-Federalists. Over the ensuing months, the proposal was debated, criticized, and expounded upon clause by clause. In the state of New York, at the time a hotbed of anti-Federalism, three delegates from the Philadelphia Convention who were also members of the Congress—Hamilton, Madison, and Jay—published a series of commentaries, now known as The Federalist Papers, in support of ratification. Before year's end, three state legislatures voted in favor of ratification. Delaware was first, voting unanimously 30-0; Pennsylvania second, approving the measure 46-23; and New Jersey third, also recording a unanimous vote. As 1788 began, Connecticut and Georgia followed Delaware's lead with almost unanimous votes, but the outcome became less certain as leaders in key states such as Virginia, New York, and Massachusetts expressed concerns over the lack of protections for people's rights. Fearing the prospect of defeat, the Federalists relented, promising that if the Constitution was adopted, amendments would be added to secure individual liberties. With that, the anti-Federalists' position collapsed. On June 21, 1788, New Hampshire became the ninth state to ratify. Three months later, on September 17, Congress adopted the Constitution as the law of the land. It then passed resolutions setting dates for choosing the first senators and representatives, the first Wednesday of January (January 7, 1789); electing the first president, the first Wednesday of February (February 4); and officially starting the new government, the first Wednesday of March (March 4), when the first Congress would convene. As its final act, the Congress of Confederation agreed to purchase 10 square miles from Maryland and Virginia for establishing a permanent capital. (Wikipedia)
RECOMMENDED READING

Pauline Maier,
Ratification: The People Debate the Constitution, 1787-1788,
Simon and Schuster,
ISBN 978-0684868547
From the Publisher: "From the distinguished historian of Revolutionary-era America and author of the acclaimed American Scripture comes this fresh and surprising account of a pivotal moment in American history—the ratification of the Constitution. When the delegates left the Constitutional Convention in Philadelphia in September 1787, the new Constitution they had written was no more than a proposal. Elected conventions in at least nine of the thirteen states would have to ratify it before it could take effect. There was reason to doubt whether that would happen. The document we revere today as the foundation of our country’s laws, the cornerstone of our legal system, was hotly disputed at the time. Some Americans denounced the Constitution for threatening the liberty that Americans had won at great cost in the Revolutionary War. One group of fiercely patriotic opponents even burned the document in a raucous public demonstration on the Fourth of July. In this splendid new history, Pauline Maier tells the dramatic story of the yearlong battle over ratification that brought such famous founders as Washington, Hamilton, Madison, Jay, and Henry together with less well-known Americans who sometimes eloquently and always passionately expressed their hopes and fears for their new country. Men argued in taverns and coffeehouses; women joined the debate in their parlors; broadsides and newspaper stories advocated various points of view and excoriated others. In small towns and counties across the country people read the document carefully and knew it well. Americans seized the opportunity to play a role in shaping the new nation. Then the ratifying conventions chosen by “We the People” scrutinized and debated the Constitution clause by clause. Although many books have been written about the Constitutional Convention, this is the first major history of ratification. It draws on a vast new collection of documents and tells the story with masterful attention to detail in a dynamic narrative. Each state’s experience was different, and Maier gives each its due even as she focuses on the four critical states of Pennsylvania, Massachusetts, Virginia, and New York, whose approval of the Constitution was crucial to its success. The New Yorker Gilbert Livingston called his participation in the ratification convention the greatest transaction of his life. The hundreds of delegates to the ratifying conventions took their responsibility seriously, and their careful inspection of the Constitution can tell us much today about a document whose meaning continues to be subject to interpretation. Ratification is the story of the founding drama of our nation, superbly told in a history that transports readers back more than two centuries to reveal the convictions and aspirations on which our country was built."
REVIEW
“The ratification of the Constitution was the most comprehensive and consequential political debate in American history. It is quite amazing that the story has never before been told with the knowledge and flair it deserves. Here Pauline Maier, one of the leading historians of the revolutionary era, at the peak of her powers, tells that story with style, wit, and incomparable mastery of the sources.”
--Joseph J. Ellis, author of First Family: Abigail and John Adams

Hamilton and Madison and Jay and Beeman,
The Federalist Papers,
Penguin Books; 1st edition (August 28, 2012),
ISBN 978-0143121978
14
Week 14: Tuesday, January 30, 2024
George Washington
WEEK 14
George Washington (February 22, 1732 – December 14, 1799) was an American military officer, statesman, and Founding Father who served as the first president of the United States from 1789 to 1797. Appointed by the Second Continental Congress as commander of the Continental Army in June 1775, Washington led Patriot forces to victory in the American Revolutionary War and then served as president of the Constitutional Convention in 1787, which drafted and ratified the Constitution of the United States and established the American federal government. Washington has been called the "Father of his Country" for his manifold leadership in the nation's founding. Washington's first public office, from 1749 to 1750, was as surveyor of Culpeper County, Virginia. He subsequently received his first military training and was assigned command of the Virginia Regiment during the French and Indian War. He was later elected to the Colony of Virginia's House of Burgesses and was named a delegate to the Continental Congress in Philadelphia, which appointed him Commander-in-Chief of the Continental Army, the Continental Army's most senior military position. As commander of the Continental Army, Washington led American forces to a decisive victory over the British in the Revolutionary War, leading the British to sign the Treaty of Paris in 1783, which acknowledged the sovereignty and independence of the Thirteen Colonies and paved the way for the establishment of the United States. He resigned his commission in 1783 after the conclusion of the Revolutionary War. Following victory in the Revolutionary War, Washington played an indispensable role in adopting and ratifying the Constitution of the United States, which replaced the Articles of Confederation in 1789 and remains the world's longest-standing written and codified national constitution to this day. He was then twice elected president by the Electoral College unanimously. As the first U.S. president, Washington implemented a strong, well-financed national government while remaining impartial in a fierce rivalry that emerged between cabinet members Thomas Jefferson and Alexander Hamilton. During the French Revolution, he proclaimed a policy of neutrality while sanctioning the Jay Treaty. He set enduring precedents for the office of president, including use of the title "Mr. President" and taking an Oath of Office with his hand on a Bible. His Farewell Address on September 19, 1796, is a preeminent statement on republicanism in which he wrote about the importance of national unity and the dangers regionalism, partisanship, and foreign influence pose to it. Upon his death on December 14, 1799, Henry Lee eulogized Washington as "first in war, first in peace, and first in the hearts of his countrymen". He has been memorialized by monuments, a federal holiday, various media depictions, geographical locations including the national capital, the State of Washington, stamps, and currency. Many scholars and ordinary Americans alike rank him among the greatest U.S. presidents. (Wikipedia)
BEST BIOGRAPHY OF GEORGE WASHINGTON
From the Publisher: "From National Book Award winner Ron Chernow, a landmark biography of George Washington. In Washington: A Life celebrated biographer Ron Chernow provides a richly nuanced portrait of the father of our nation. With a breadth and depth matched by no other one-volume life of Washington, this crisply paced narrative carries the reader through his troubled boyhood, his precocious feats in the French and Indian War, his creation of Mount Vernon, his heroic exploits with the Continental Army, his presiding over the Constitutional Convention, and his magnificent performance as America's first president. Despite the reverence his name inspires, Washington remains a lifeless waxwork for many Americans, worthy but dull. A laconic man of granite self-control, he often arouses more respect than affection. In this groundbreaking work, based on massive research, Chernow dashes forever the stereotype of a stolid, unemotional man. A strapping six feet, Washington was a celebrated horseman, elegant dancer, and tireless hunter, with a fiercely guarded emotional life. Chernow brings to vivid life a dashing, passionate man of fiery opinions and many moods. Probing his private life, he explores his fraught relationship with his crusty mother, his youthful infatuation with the married Sally Fairfax, and his often conflicted feelings toward his adopted children and grandchildren. He also provides a lavishly detailed portrait of his marriage to Martha and his complex behavior as a slave master. At the same time, Washington is an astute and surprising portrait of a canny political genius who knew how to inspire people. Not only did Washington gather around himself the foremost figures of the age, including James Madison, Alexander Hamilton, John Adams, and Thomas Jefferson, but he also brilliantly orchestrated their actions to shape the new federal government, define the separation of powers, and establish the office of the presidency. In this unique biography, Ron Chernow takes us on a page-turning journey through all the formative events of America's founding. With a dramatic sweep worthy of its giant subject, Washington is a magisterial work from one of our most elegant storytellers."
15
Week 15: Tuesday, February 6, 2024
Alexander Hamilton
WEEK 15
During the Revolution, Hamilton, while still in his early twenties, Hamilton became George Washington’s chief aide and played a heroic role in several battles, including the one that forced the surrender of General Cornwallis at Yorktown. Like the commander-in-chief, Hamilton thought "continentally," and he was so good at reading Washington's mind that the general trusted him to manage his correspondence and even to write his orders. And that was just the beginning of Hamilton's brilliant career.
BEST BIOGRAPHY OF HAMILTON
The #1 New York Times bestseller, and the inspiration for the hit Broadway musical Hamilton!
Pulitzer Prize-winning author Ron Chernow presents a landmark biography of Alexander Hamilton, the Founding Father who galvanized, inspired, scandalized, and shaped the newborn nation.
"Grand-scale biography at its best—thorough, insightful, consistently fair, and superbly written . . . A genuinely great book." —David McCullough
“A robust full-length portrait, in my view the best ever written, of the most brilliant, charismatic and dangerous founder of them all." —Joseph Ellis
Few figures in American history have been more hotly debated or more grossly misunderstood than Alexander Hamilton. Chernow’s biography gives Hamilton his due and sets the record straight, deftly illustrating that the political and economic greatness of today’s America is the result of Hamilton’s countless sacrifices to champion ideas that were often wildly disputed during his time. “To repudiate his legacy,” Chernow writes, “is, in many ways, to repudiate the modern world.” Chernow here recounts Hamilton’s turbulent life: an illegitimate, largely self-taught orphan from the Caribbean, he came out of nowhere to take America by storm, rising to become George Washington’s aide-de-camp in the Continental Army, coauthoring The Federalist Papers, founding the Bank of New York, leading the Federalist Party, and becoming the first Treasury Secretary of the United States.Historians have long told the story of America’s birth as the triumph of Jefferson’s democratic ideals over the aristocratic intentions of Hamilton. Chernow presents an entirely different man, whose legendary ambitions were motivated not merely by self-interest but by passionate patriotism and a stubborn will to build the foundations of American prosperity and power. His is a Hamilton far more human than we’ve encountered before—from his shame about his birth to his fiery aspirations, from his intimate relationships with childhood friends to his titanic feuds with Jefferson, Madison, Adams, Monroe, and Burr, and from his highly public affair with Maria Reynolds to his loving marriage to his loyal wife Eliza. And never before has there been a more vivid account of Hamilton’s famous and mysterious death in a duel with Aaron Burr in July of 1804.
Chernow’s biography is not just a portrait of Hamilton, but the story of America’s birth seen through its most central figure. At a critical time to look back to our roots, Alexander Hamilton will remind readers of the purpose of our institutions and our heritage as Americans.
16
Week 16: Tuesday, February 13, 2024
Thomas Jefferson
WEEK 16
 Thomas Jefferson (1743–1826) was an American statesman, diplomat, lawyer, architect, philosopher, and Founding Father who served as the third president of the United States from 1801 to 1809.He was the primary author of the Declaration of Independence. Following the American Revolutionary War and prior to becoming president in 1801, Jefferson was the nation's first U.S. secretary of state under George Washington and then the nation's second vice president under John Adams. During the American Revolution, Jefferson represented Virginia at the Second Continental Congress and served as the second governor of Virginia from 1779 to 1781. In 1785, Congress appointed Jefferson U.S. minister to France, where he served from 1785 to 1789. President Washington then appointed Jefferson the nation's first secretary of state, where he served from 1790 to 1793. During this time, in the early 1790s, Jefferson and James Madison organized the Democratic-Republican Party to oppose the Federalist Party during the formation of the nation's First Party System. Jefferson and Federalist John Adams became both friends and political rivals. In the 1796 U.S. presidential election between the two, Jefferson came in second, which made him Adams' vice president under the electoral laws of the time. Four years later, in the 1800 presidential election, Jefferson again challenged Adams, and won the presidency. In 1804, Jefferson was reelected overwhelmingly to a second term. As president, Jefferson assertively defended the nation's shipping and trade interests against Barbary pirates and aggressive British trade policies. Beginning in 1803, he promoted a western expansionist policy with the Louisiana Purchase, which doubled the nation's geographic size. To make room for settlement, Jefferson began the process of Indian tribal removal from the newly acquired territory. As a result of peace negotiations with France, Jefferson was able to reduce military forces and expenditures. In his second presidential term, Jefferson was beset by difficulties at home, including the trial of his former vice president Aaron Burr. In 1807, American foreign trade was diminished when Jefferson implemented the Embargo Act to defend the nation's industries from British threats to U.S. shipping.
Thomas Jefferson (1743–1826) was an American statesman, diplomat, lawyer, architect, philosopher, and Founding Father who served as the third president of the United States from 1801 to 1809.He was the primary author of the Declaration of Independence. Following the American Revolutionary War and prior to becoming president in 1801, Jefferson was the nation's first U.S. secretary of state under George Washington and then the nation's second vice president under John Adams. During the American Revolution, Jefferson represented Virginia at the Second Continental Congress and served as the second governor of Virginia from 1779 to 1781. In 1785, Congress appointed Jefferson U.S. minister to France, where he served from 1785 to 1789. President Washington then appointed Jefferson the nation's first secretary of state, where he served from 1790 to 1793. During this time, in the early 1790s, Jefferson and James Madison organized the Democratic-Republican Party to oppose the Federalist Party during the formation of the nation's First Party System. Jefferson and Federalist John Adams became both friends and political rivals. In the 1796 U.S. presidential election between the two, Jefferson came in second, which made him Adams' vice president under the electoral laws of the time. Four years later, in the 1800 presidential election, Jefferson again challenged Adams, and won the presidency. In 1804, Jefferson was reelected overwhelmingly to a second term. As president, Jefferson assertively defended the nation's shipping and trade interests against Barbary pirates and aggressive British trade policies. Beginning in 1803, he promoted a western expansionist policy with the Louisiana Purchase, which doubled the nation's geographic size. To make room for settlement, Jefferson began the process of Indian tribal removal from the newly acquired territory. As a result of peace negotiations with France, Jefferson was able to reduce military forces and expenditures. In his second presidential term, Jefferson was beset by difficulties at home, including the trial of his former vice president Aaron Burr. In 1807, American foreign trade was diminished when Jefferson implemented the Embargo Act to defend the nation's industries from British threats to U.S. shipping.(Wikipedia)
RECOMMENDED READING
17
Week 17: Tuesday, February 20, 2024
Louisiana Purchase
WEEK 17
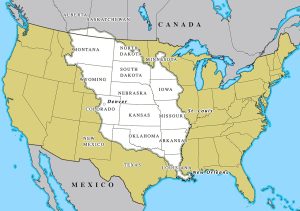 The Louisiana Purchase was the acquisition of the territory of Louisiana by the United States from the French First Republic in 1803. This consisted of most of the land in the Mississippi River's drainage basin west of the river. In return for fifteen million dollars, or approximately eighteen dollars per square mile, the United States nominally acquired a total of 828,000 sq mi in Middle America. However, France only controlled a small fraction of this area, most of which was inhabited by Native Americans; effectively, for the majority of the area, the United States bought the preemptive right to obtain Indian lands by treaty or by conquest, to the exclusion of other colonial powers. The Kingdom of France had controlled the Louisiana territory from 1682 until it was ceded to Spain in 1762. In 1800, Napoleon, the First Consul of the French Republic, regained ownership of Louisiana in exchange for Tuscany as part of a broader effort to re-establish a French colonial empire in North America. However, France's failure to suppress a revolt in Saint-Domingue, coupled with the prospect of renewed warfare with the United Kingdom, prompted Napoleon to consider selling Louisiana to the United States. Acquisition of Louisiana was a long-term goal of President Thomas Jefferson, who was especially eager to gain control of the crucial Mississippi River port of New Orleans. Jefferson tasked James Monroe and Robert R. Livingston with purchasing New Orleans. Negotiating with French Treasury Minister François Barbé-Marbois, the U.S. representatives quickly agreed to purchase the entire territory of Louisiana after it was offered. Overcoming the opposition of the Federalist Party, Jefferson and Secretary of State James Madison persuaded Congress to ratify and fund the Louisiana Purchase.(Wikipedia)
The Louisiana Purchase was the acquisition of the territory of Louisiana by the United States from the French First Republic in 1803. This consisted of most of the land in the Mississippi River's drainage basin west of the river. In return for fifteen million dollars, or approximately eighteen dollars per square mile, the United States nominally acquired a total of 828,000 sq mi in Middle America. However, France only controlled a small fraction of this area, most of which was inhabited by Native Americans; effectively, for the majority of the area, the United States bought the preemptive right to obtain Indian lands by treaty or by conquest, to the exclusion of other colonial powers. The Kingdom of France had controlled the Louisiana territory from 1682 until it was ceded to Spain in 1762. In 1800, Napoleon, the First Consul of the French Republic, regained ownership of Louisiana in exchange for Tuscany as part of a broader effort to re-establish a French colonial empire in North America. However, France's failure to suppress a revolt in Saint-Domingue, coupled with the prospect of renewed warfare with the United Kingdom, prompted Napoleon to consider selling Louisiana to the United States. Acquisition of Louisiana was a long-term goal of President Thomas Jefferson, who was especially eager to gain control of the crucial Mississippi River port of New Orleans. Jefferson tasked James Monroe and Robert R. Livingston with purchasing New Orleans. Negotiating with French Treasury Minister François Barbé-Marbois, the U.S. representatives quickly agreed to purchase the entire territory of Louisiana after it was offered. Overcoming the opposition of the Federalist Party, Jefferson and Secretary of State James Madison persuaded Congress to ratify and fund the Louisiana Purchase.(Wikipedia)
18
Week 18: Tuesday, February 27, 2024
James Madison
WEEK 18
 James Madison (1751–1836) was an American statesman, diplomat, and Founding Father who served as the fourth president of the United States from 1809 to 1817. Madison was popularly acclaimed the "Father of the Constitution" for his pivotal role in drafting and promoting the Constitution of the United States and the Bill of Rights. Madison was born into a prominent slave-owning planter family in Virginia. He served as a member of the Virginia House of Delegates and the Continental Congress during and after the American Revolutionary War. Dissatisfied with the weak national government established by the Articles of Confederation, he helped organize the Constitutional Convention, which produced a new constitution designed to strengthen republican government against democratic assembly. Madison's Virginia Plan was the basis for the convention's deliberations, and he was an influential voice at the convention. He became one of the leaders in the movement to ratify the Constitution and joined Alexander Hamilton and John Jay in writing The Federalist Papers, a series of pro-ratification essays that remains prominent among works of political science in American history. Madison emerged as an important leader in the House of Representatives and was a close adviser to President George Washington. During the early 1790s, Madison opposed the economic program and the accompanying centralization of power favored by Secretary of the Treasury Hamilton. Alongside Thomas Jefferson, he organized the Democratic–Republican Party in opposition to Hamilton's Federalist Party. After Jefferson was elected president in 1800, Madison served as his Secretary of State from 1801 to 1809 and supported Jefferson in the case of Marbury v. Madison. While Madison was Secretary of State, Jefferson made the Louisiana Purchase, and later, as President, Madison oversaw related disputes in the Northwest Territories. Madison was elected president in 1808. Motivated by desire to acquire land held by Britain, Spain, and Native Americans, and after diplomatic protests with a trade embargo failed to end British seizures of American shipped goods, Madison led the United States into the War of 1812. Although the war ended inconclusively, many Americans viewed the war's outcome as a successful "second war of independence" against Britain. Madison was re-elected in 1812, albeit by a smaller margin. The war convinced Madison of the necessity of a stronger federal government. He presided over the creation of the Second Bank of the United States and the enactment of the protective Tariff of 1816. By treaty or through war, Native American tribes ceded 26,000,000 acres (11,000,000 ha) of land to the United States under Madison's presidency. Retiring from public office at the end of his presidency in 1817, Madison returned to his plantation, Montpelier, and died there in 1836. During his lifetime, Madison was a slave owner. In 1783, to prevent a slave rebellion at Montpelier, Madison freed one of his slaves. He did not free any slaves in his will. Among historians, Madison is considered one of the most important Founding Fathers of the United States. Leading historians have generally ranked him as an above-average president, although they are critical of his endorsement of slavery and his leadership during the War of 1812. Madison's name is commemorated in many landmarks across the nation, both publicly and privately, with prominent examples including Madison Square Garden, James Madison University, the James Madison Memorial Building, and the USS James Madison.(Wikipedia)
James Madison (1751–1836) was an American statesman, diplomat, and Founding Father who served as the fourth president of the United States from 1809 to 1817. Madison was popularly acclaimed the "Father of the Constitution" for his pivotal role in drafting and promoting the Constitution of the United States and the Bill of Rights. Madison was born into a prominent slave-owning planter family in Virginia. He served as a member of the Virginia House of Delegates and the Continental Congress during and after the American Revolutionary War. Dissatisfied with the weak national government established by the Articles of Confederation, he helped organize the Constitutional Convention, which produced a new constitution designed to strengthen republican government against democratic assembly. Madison's Virginia Plan was the basis for the convention's deliberations, and he was an influential voice at the convention. He became one of the leaders in the movement to ratify the Constitution and joined Alexander Hamilton and John Jay in writing The Federalist Papers, a series of pro-ratification essays that remains prominent among works of political science in American history. Madison emerged as an important leader in the House of Representatives and was a close adviser to President George Washington. During the early 1790s, Madison opposed the economic program and the accompanying centralization of power favored by Secretary of the Treasury Hamilton. Alongside Thomas Jefferson, he organized the Democratic–Republican Party in opposition to Hamilton's Federalist Party. After Jefferson was elected president in 1800, Madison served as his Secretary of State from 1801 to 1809 and supported Jefferson in the case of Marbury v. Madison. While Madison was Secretary of State, Jefferson made the Louisiana Purchase, and later, as President, Madison oversaw related disputes in the Northwest Territories. Madison was elected president in 1808. Motivated by desire to acquire land held by Britain, Spain, and Native Americans, and after diplomatic protests with a trade embargo failed to end British seizures of American shipped goods, Madison led the United States into the War of 1812. Although the war ended inconclusively, many Americans viewed the war's outcome as a successful "second war of independence" against Britain. Madison was re-elected in 1812, albeit by a smaller margin. The war convinced Madison of the necessity of a stronger federal government. He presided over the creation of the Second Bank of the United States and the enactment of the protective Tariff of 1816. By treaty or through war, Native American tribes ceded 26,000,000 acres (11,000,000 ha) of land to the United States under Madison's presidency. Retiring from public office at the end of his presidency in 1817, Madison returned to his plantation, Montpelier, and died there in 1836. During his lifetime, Madison was a slave owner. In 1783, to prevent a slave rebellion at Montpelier, Madison freed one of his slaves. He did not free any slaves in his will. Among historians, Madison is considered one of the most important Founding Fathers of the United States. Leading historians have generally ranked him as an above-average president, although they are critical of his endorsement of slavery and his leadership during the War of 1812. Madison's name is commemorated in many landmarks across the nation, both publicly and privately, with prominent examples including Madison Square Garden, James Madison University, the James Madison Memorial Building, and the USS James Madison.(Wikipedia)
19
Week 19: Tuesday, March 5, 2024
James Monroe
WEEK 19
 James Monroe (1758–July 4, 1831) was an American statesman, lawyer, diplomat, and Founding Father who served as the fifth president of the United States from 1817 to 1825, a member of the Democratic-Republican Party. He was the last Founding Father to serve as president as well as the last president of the Virginia dynasty and the Republican Generation. His presidency coincided with the Era of Good Feelings, concluding the First Party System era of American politics. He is best known for issuing the Monroe Doctrine, a policy of limiting European colonialism in the Americas. Previously he served as governor of Virginia, a member of the United States Senate, U.S. ambassador to France and Britain, the seventh secretary of state, and the eighth secretary of war. Monroe served in the Continental Army during the American Revolutionary War. He studied law under Thomas Jefferson from 1780 to 1783 and served as a delegate in the Continental Congress as well as a delegate to the Virginia Ratifying Convention. He opposed the ratification of the United States Constitution. In 1790, he won election to the Senate where he became a leader of the Democratic-Republican Party. He left the Senate in 1794 to serve as President George Washington's ambassador to France but was recalled by Washington in 1796. Monroe won the election as Governor of Virginia in 1799 and strongly supported Jefferson's candidacy in the 1800 presidential election. As President Jefferson's special envoy, Monroe helped negotiate the Louisiana Purchase, through which the United States nearly doubled in size. Monroe fell out with his longtime friend James Madison after Madison rejected the Monroe–Pinkney Treaty that Monroe negotiated with Britain. He unsuccessfully challenged Madison for the Democratic-Republican nomination in the 1808 presidential election, but he joined Madison's administration as Secretary of State in 1811. During the later stages of the War of 1812, Monroe simultaneously served as Madison's Secretary of State and Secretary of War. Monroe's wartime leadership established him as Madison's heir apparent, and he easily defeated Federalist candidate Rufus King in the 1816 presidential election. During Monroe's tenure as president, the Federalist Party collapsed as a national political force and Monroe was re-elected, virtually unopposed, in 1820. As president, Monroe signed the Missouri Compromise, which admitted Missouri as a slave state and banned slavery from territories north of the 36°30′ parallel. In foreign affairs, Monroe and Secretary of State John Quincy Adams favored a policy of conciliation with Britain and a policy of expansionism against the Spanish Empire. In the 1819 Adams–Onís Treaty with Spain, the United States secured Florida and established its western border with New Spain. In 1823, Monroe announced the United States' opposition to any European intervention in the recently independent countries of the Americas with the Monroe Doctrine, which became a landmark in American foreign policy. Monroe was a member of the American Colonization Society which supported the colonization of Africa by freed slaves, and Liberia's capital of Monrovia is named in his honor. Following his retirement in 1825, Monroe was plagued by financial difficulties and died on July 4, 1831, in New York City—sharing a distinction with Presidents John Adams and Thomas Jefferson of dying on the anniversary of U.S. independence. (Wikipedia)
James Monroe (1758–July 4, 1831) was an American statesman, lawyer, diplomat, and Founding Father who served as the fifth president of the United States from 1817 to 1825, a member of the Democratic-Republican Party. He was the last Founding Father to serve as president as well as the last president of the Virginia dynasty and the Republican Generation. His presidency coincided with the Era of Good Feelings, concluding the First Party System era of American politics. He is best known for issuing the Monroe Doctrine, a policy of limiting European colonialism in the Americas. Previously he served as governor of Virginia, a member of the United States Senate, U.S. ambassador to France and Britain, the seventh secretary of state, and the eighth secretary of war. Monroe served in the Continental Army during the American Revolutionary War. He studied law under Thomas Jefferson from 1780 to 1783 and served as a delegate in the Continental Congress as well as a delegate to the Virginia Ratifying Convention. He opposed the ratification of the United States Constitution. In 1790, he won election to the Senate where he became a leader of the Democratic-Republican Party. He left the Senate in 1794 to serve as President George Washington's ambassador to France but was recalled by Washington in 1796. Monroe won the election as Governor of Virginia in 1799 and strongly supported Jefferson's candidacy in the 1800 presidential election. As President Jefferson's special envoy, Monroe helped negotiate the Louisiana Purchase, through which the United States nearly doubled in size. Monroe fell out with his longtime friend James Madison after Madison rejected the Monroe–Pinkney Treaty that Monroe negotiated with Britain. He unsuccessfully challenged Madison for the Democratic-Republican nomination in the 1808 presidential election, but he joined Madison's administration as Secretary of State in 1811. During the later stages of the War of 1812, Monroe simultaneously served as Madison's Secretary of State and Secretary of War. Monroe's wartime leadership established him as Madison's heir apparent, and he easily defeated Federalist candidate Rufus King in the 1816 presidential election. During Monroe's tenure as president, the Federalist Party collapsed as a national political force and Monroe was re-elected, virtually unopposed, in 1820. As president, Monroe signed the Missouri Compromise, which admitted Missouri as a slave state and banned slavery from territories north of the 36°30′ parallel. In foreign affairs, Monroe and Secretary of State John Quincy Adams favored a policy of conciliation with Britain and a policy of expansionism against the Spanish Empire. In the 1819 Adams–Onís Treaty with Spain, the United States secured Florida and established its western border with New Spain. In 1823, Monroe announced the United States' opposition to any European intervention in the recently independent countries of the Americas with the Monroe Doctrine, which became a landmark in American foreign policy. Monroe was a member of the American Colonization Society which supported the colonization of Africa by freed slaves, and Liberia's capital of Monrovia is named in his honor. Following his retirement in 1825, Monroe was plagued by financial difficulties and died on July 4, 1831, in New York City—sharing a distinction with Presidents John Adams and Thomas Jefferson of dying on the anniversary of U.S. independence. (Wikipedia)
RECOMMENDED READING
20
Week 20: Tuesday, March 12, 2024
John Quincy Adams
WEEK 20
RECOMMENDED READING

James Traub,
John Quincy Adams: Militant Spirit,
Basic Books; Reprint edition (October 10, 2017),
ISBN 978-0465093830
All
Week 11: Tue., Jan. 9, 2024
What Kind of Revolution?
WEEK 11
What Kind of a Revolution Did We get?
Gordon Wood: "Americans were not born free and democratic in any modern sense; they became so—and largely as a consequence of the American Revolution. After eighteenth-century Americans threw off their monarchical allegiance in 1776, they struggled to find new attachments befitting a republican people. Living in a society that was already diverse and pluralistic, Americans realized that these attachments could not be the traditional ethnic, religious, and tribal loyalties of the Old World. Instead, they sought new enlightened connections to hold their new popular societies together. But when these proved too idealistic and visionary, they eventually found new democratic adhesives in the actual behavior of plain ordinary people—in the everyday desire for the freedom to make money and pursue happiness in the here and now. To base a society on the commonplace behavior of ordinary people may be obvious and understandable to us today, but it was momentously radical in the long sweep of world history up to that time. This book attempts to explain this momentous radicalism of the American Revolution."
Gordon Wood, The Radicalism of the American Revolution (p. 2). Knopf Doubleday Publishing Group.
RECOMMENDED READING

Gordon S. Wood,
The Radicalism of the American Revolution,
Vintage; Reprint edition (March 2, 1993),
ISBN 978-0679736882
REQUIRED READING FOR THE WHOLE YEAR OF HISTORY OF THE USA
Wilfred McClay, Land of Hope:
"There were unsettling questions for the Americans about the revolutionary journey on which they found themselves embarked. What sort of effect was this war having on the social and political life of the colonies-becoming-a-nation? How was it changing things? If this was to be a revolution, how thoroughgoing a revolution was it to be? Was, in fact, the world being turned upside down – or merely right side up? The latter might have seemed more likely. As we’ve seen, the most influential justifications offered in favor of revolution invoked not radical change but rather restoration – restoring and protecting the colonists’ customary rights as Englishmen – as the pretext for revolution. But like any great historical event, the American Revolution was complicated, with many aspects. Even those fighting on the same side sometimes saw the cause differently. To a greater extent than many of us appreciate today, the Revolutionary War took on many of the aspects of a civil war, pitting Loyalists against Patriots; dividing families, towns, regions, and social classes; and producing fierce struggles over fundamental political and social values.values. Loyalty to the Crown had been the instinctive response of a sizable minority of Americans. But for some, the resonant words of the Declaration of Independence pointed toward a larger aspiration, something more than mere restoration. Such an interpretation pointed toward the emergence on the world stage of something genuinely new: a republican order built upon a principled commitment to both equality and liberty. Historians have been arguing for generations which of these different tendencies was dominant and hence which offers us the best way to think about the Revolution. Was the Revolution essentially conservative in its objectives, merely seeking to separate America from Britain to return the political order to what it had been before the disruptions caused by clumsy and wrongheaded British colonial policies? Or was it something radical, in the sense of wishing to shake things up, dramatically and fundamentally upending the entrenched inequalities and hierarchies in society, and not merely changing the names and faces of those at the top of the political structure? As the American historian Carl Becker, who strongly advocated for the latter view, put it memorably more than a hundred years ago, “the war was not about home rule, but about who would rule at home.”
McClay, Wilfred M.. Land of Hope (pp. 58-59). Encounter Books.
RECOMMENDED READING

Gordon Wood,
Empire of Liberty,
Oxford University Press; 1st edition (October 28, 2009),
ISBN 978-0195039146
Week 12: Tue., Jan. 16, 2024
Writing the Constitution
WEEK 12
The Constitution of the United States is the supreme law of the United States of America. It superseded the Articles of Confederation, the nation's first constitution, in 1789. Originally comprising seven articles, it delineates the national frame and constraints of government. The Constitution's first three articles embody the doctrine of the separation of powers, whereby the federal government is divided into three branches: the legislative, consisting of the bicameral Congress (Article I); the executive, consisting of the president and subordinate officers (Article II); and the judicial, consisting of the Supreme Court and other federal courts (Article III). Article IV, Article V, and Article VI embody concepts of federalism, describing the rights and responsibilities of state governments, the states in relationship to the federal government, and the shared process of constitutional amendment. Article VII establishes the procedure subsequently used by the 13 states to ratify it. The Constitution of the United States is the oldest and longest-standing written and codified national constitution in force in the world today. The drafting of the Constitution, often referred to as its framing, was completed at the Constitutional Convention, which assembled at Independence Hall in Philadelphia between May 25 and September 17, 1787. Delegates to the convention were chosen by the state legislatures of 12 of the 13 original states; Rhode Island refused to send delegates. The convention's initial mandate was limited to amending the Articles of Confederation, which had proven highly ineffective in meeting the young nation's needs. Almost immediately, however, delegates began considering measures to replace the Articles. The first proposal discussed, introduced by delegates from Virginia, called for a bicameral (two-house) Congress that was to be elected on a proportional basis based on state population, an elected chief executive, and an appointed judicial branch. An alternative to the Virginia Plan, known as the New Jersey Plan, also called for an elected executive but retained the legislative structure created by the Articles, a unicameral Congress where all states had one vote. On June 19, 1787, delegates rejected the New Jersey Plan with three states voting in favor, seven against, and one divided. The plan's defeat led to a series of compromises centering primarily on two issues: slavery and proportional representation. The first of these pitted Northern states, where slavery was slowly being abolished, against Southern states, whose agricultural economies depended on slave labor. The issue of proportional representation was of similar concern to less populous states, which under the Articles had the same power as larger states. To satisfy interests in the South, particularly in Georgia and South Carolina, the delegates agreed to protect the slave trade, that is, the importation of slaves, for 20 years. Slavery was protected further by allowing states to count three-fifths of their slaves as part of their populations, for the purpose of representation in the federal government, and by requiring the return of escaped slaves to their owners, even if captured in states where slavery had been abolished. Finally, the delegates adopted the Connecticut Compromise, which proposed a Congress with proportional representation in the lower house and equal representation in the upper house (the Senate) giving each state two senators. While these compromises held the Union together and aided the Constitution's ratification, slavery continued for six more decades and the less populous states continue to have disproportional representation in the U.S. Senate and Electoral College.(Wikipedia)
RECOMMENDED READING

Carol Berkin,
A Brilliant Solution: Inventing the American Constitution,
Harcourt; First Edition (September 13, 2002),
ISBN 978-0151009480
Historian Carol Berkin's A Brilliant Solution: Inventing the American Constitution is a rich narrative portrait of post-revolutionary America and the men who shaped its political future.
"Just as the Constitution was a brilliant solution to the problems of the 1780s, Carol Berkin's book is a brilliant account of the making of that constitution. Written with great verve and clarity, it nicely captures all the contingency and unpredictability in the framing of the Constitution."—Pulitzer Prize-winning author Gordon S. Wood
Though the American Revolution is widely recognized as our nation's founding story, the years immediately following the war — when our government was a disaster and the country was in a terrible crisis — were in fact the most crucial in establishing the country's independence. The group of men who traveled to Philadelphia in the summer of 1787 had no idea what kind of history their meeting would make. But all their ideas, arguments, and compromises — from the creation of the Constitution itself, article by article, to the insistence that it remain a living, evolving document — laid the foundation for a government that has surpassed the founders' greatest hopes. Revisiting all the original historical documents of the period and drawing from her deep knowledge of eighteenth-century politics, Carol Berkin opens up the hearts and minds of America's founders, revealing the issues they faced, the times they lived in, and their humble expectations of success.Note: The new hardcovers available from Amazon, offer a much better price for value than the paperback edition.
RECOMMENDED READING
From the Publisher: "New York Times bestseller and Pulitzer Prize-winning author Gordon S. Wood elucidates the debates over the founding documents of the United States.
The half century extending from the imperial crisis between Britain and its colonies in the 1760s to the early decades of the new republic of the United States was the greatest and most creative era of constitutionalism in American history, and perhaps in the world. During these decades, Americans explored and debated all aspects of politics and constitutionalism--the nature of power, liberty, representation, rights, the division of authority between different spheres of government, sovereignty, judicial authority, and written constitutions. The results of these issues produced institutions that have lasted for over two centuries. In this new book, eminent historian Gordon S. Wood distills a lifetime of work on constitutional innovations during the Revolutionary era. In concise form, he illuminates critical events in the nation's founding, ranging from the imperial debate that led to the Declaration of Independence to the revolutionary state constitution making in 1776 and the creation of the Federal Constitution in 1787. Among other topics, he discusses slavery and constitutionalism, the emergence of the judiciary as one of the major tripartite institutions of government, the demarcation between public and private, and the formation of states' rights. Here is an immensely readable synthesis of the key era in the making of the history of the United States, presenting timely insights on the Constitution and the nation's foundational legal and political documents"
REVIEWS
"No one has done more to teach us about the origins of American constitutionalism than Gordon S. Wood. Now, at a moment when we are trembling over the strength of our constitutional system, Wood gives us a deft shorthand account of how it all began. For anyone who wants to understand what made American constitutionalism such a vital political experiment, this is the place to start." -- Jack Rakove, author of Beyond Belief, Beyond Conscience: The Radical Significance of the Free Exercise of Religion
"Gordon Wood has packed a lifetime of learning into this splendid little volume. In his capable hands, our founding charters, grown stale from familiarity, regain their freshness and allure as revolutionary documents that redefined our politics. Wood has an uncanny ability to project himself into the past and to report on his findings as if he had been a personal witness to those distant events." -- Ron Chernow, author of Alexander Hamilton
"Masterful... No historian knows more about the founding years of the U.S. than Wood. In his latest, he once again demonstrates his characteristic clarity... A fresh, lucid distillation of Wood's vast learning about the origins of American government." --Kirkus, Starred Review
"No living historian has done more to illuminate the origins of our constitutional heritage in the Revolutionary era."--National Review
REQUIRED READING FOR THE WHOLE YEAR OF HISTORY OF THE USA
From the Publisher:
"For too long we’ve lacked a compact, inexpensive, authoritative, and compulsively readable book that offers American readers a clear, informative, and inspiring narrative account of their country. Such a fresh retelling of the American story is especially needed today, to shape and deepen young Americans’ sense of the land they inhabit, help them to understand its roots and share in its memories, all the while equipping them for the privileges and responsibilities of citizenship in American society. The existing texts simply fail to tell that story with energy and conviction. Too often they reflect a fragmented outlook that fails to convey to American readers the grand trajectory of their own history. A great nation needs and deserves a great and coherent narrative, as an expression of its own self-understanding and its aspirations; and it needs to be able to convey that narrative effectively. Of course, it goes without saying that such a narrative cannot be a fairy tale of the past. It will not be convincing if it is not truthful. But as Land of Hope brilliantly shows, there is no contradiction between a truthful account of the American past and an inspiring one. Readers of Land of Hope will find both in its pages."
REVIEWS
“At a time of severe partisanship that has infected many accounts of our nation’s past, this brilliant new history, Land of Hope, written in lucid and often lyrical prose, is much needed. It is accurate, honest, and free of the unhistorical condescension so often paid to the people of America’s past. This generous but not uncritical story of our nation’s history ought to be read by every American. It explains and justifies the right kind of patriotism.”― Gordon S. Wood, author of Friends Divided: John Adams and Thomas Jefferson
“We’ve long needed a readable text that truly tells the American story, neither hiding the serious injustices in our history nor soft-pedaling our nation’s extraordinary achievements. Such a text cannot be a mere compilation of facts, and it certainly could not be written by someone lacking a deep understanding and appreciation of America’s constitutional ideals and institutions. Bringing his impressive skills as a political theorist, historian, and writer to bear, Wilfred McClay has supplied the need.”― Robert P. George, McCormick Professor of Jurisprudence, Princeton University
“No one has told the story of America with greater balance or better prose than Wilfred McClay. Land of Hope is a history book that you will not be able to put down. From the moment that ‘natives’ first crossed here over the Bering Strait, to the founding of America’s great experiment in republican government, to the horror and triumph of the Civil War...McClay’s account will capture your attention while offering an unforgettable education.”― James W. Ceaser, Professor of Politics, University of Virginia
Week 13: Tue., Jan. 23, 2024
Ratifying the Constitution
WEEK 13
Within three days of its signing on September 17, 1787, the Constitution was submitted to the Congress of the Confederation, then sitting in New York City, the nation's temporary capital.The document, originally intended as a revision of the Articles of Confederation, instead introduced a completely new form of government. While members of Congress had the power to reject it, they voted unanimously on September 28 to forward the proposal to the thirteen states for their ratification. Under the process outlined in Article VII of the proposed Constitution, the state legislatures were tasked with organizing "Federal Conventions" to ratify the document. This process ignored the amendment provision of the Articles of Confederation which required unanimous approval of all the states. Instead, Article VII called for ratification by just nine of the 13 states—a two-thirds majority. Two factions soon emerged, one supporting the Constitution, the Federalists, and the other opposing it, the so-called Anti-Federalists. Over the ensuing months, the proposal was debated, criticized, and expounded upon clause by clause. In the state of New York, at the time a hotbed of anti-Federalism, three delegates from the Philadelphia Convention who were also members of the Congress—Hamilton, Madison, and Jay—published a series of commentaries, now known as The Federalist Papers, in support of ratification. Before year's end, three state legislatures voted in favor of ratification. Delaware was first, voting unanimously 30-0; Pennsylvania second, approving the measure 46-23; and New Jersey third, also recording a unanimous vote. As 1788 began, Connecticut and Georgia followed Delaware's lead with almost unanimous votes, but the outcome became less certain as leaders in key states such as Virginia, New York, and Massachusetts expressed concerns over the lack of protections for people's rights. Fearing the prospect of defeat, the Federalists relented, promising that if the Constitution was adopted, amendments would be added to secure individual liberties. With that, the anti-Federalists' position collapsed. On June 21, 1788, New Hampshire became the ninth state to ratify. Three months later, on September 17, Congress adopted the Constitution as the law of the land. It then passed resolutions setting dates for choosing the first senators and representatives, the first Wednesday of January (January 7, 1789); electing the first president, the first Wednesday of February (February 4); and officially starting the new government, the first Wednesday of March (March 4), when the first Congress would convene. As its final act, the Congress of Confederation agreed to purchase 10 square miles from Maryland and Virginia for establishing a permanent capital. (Wikipedia)
RECOMMENDED READING

Pauline Maier,
Ratification: The People Debate the Constitution, 1787-1788,
Simon and Schuster,
ISBN 978-0684868547
From the Publisher: "From the distinguished historian of Revolutionary-era America and author of the acclaimed American Scripture comes this fresh and surprising account of a pivotal moment in American history—the ratification of the Constitution. When the delegates left the Constitutional Convention in Philadelphia in September 1787, the new Constitution they had written was no more than a proposal. Elected conventions in at least nine of the thirteen states would have to ratify it before it could take effect. There was reason to doubt whether that would happen. The document we revere today as the foundation of our country’s laws, the cornerstone of our legal system, was hotly disputed at the time. Some Americans denounced the Constitution for threatening the liberty that Americans had won at great cost in the Revolutionary War. One group of fiercely patriotic opponents even burned the document in a raucous public demonstration on the Fourth of July. In this splendid new history, Pauline Maier tells the dramatic story of the yearlong battle over ratification that brought such famous founders as Washington, Hamilton, Madison, Jay, and Henry together with less well-known Americans who sometimes eloquently and always passionately expressed their hopes and fears for their new country. Men argued in taverns and coffeehouses; women joined the debate in their parlors; broadsides and newspaper stories advocated various points of view and excoriated others. In small towns and counties across the country people read the document carefully and knew it well. Americans seized the opportunity to play a role in shaping the new nation. Then the ratifying conventions chosen by “We the People” scrutinized and debated the Constitution clause by clause. Although many books have been written about the Constitutional Convention, this is the first major history of ratification. It draws on a vast new collection of documents and tells the story with masterful attention to detail in a dynamic narrative. Each state’s experience was different, and Maier gives each its due even as she focuses on the four critical states of Pennsylvania, Massachusetts, Virginia, and New York, whose approval of the Constitution was crucial to its success. The New Yorker Gilbert Livingston called his participation in the ratification convention the greatest transaction of his life. The hundreds of delegates to the ratifying conventions took their responsibility seriously, and their careful inspection of the Constitution can tell us much today about a document whose meaning continues to be subject to interpretation. Ratification is the story of the founding drama of our nation, superbly told in a history that transports readers back more than two centuries to reveal the convictions and aspirations on which our country was built."
REVIEW
“The ratification of the Constitution was the most comprehensive and consequential political debate in American history. It is quite amazing that the story has never before been told with the knowledge and flair it deserves. Here Pauline Maier, one of the leading historians of the revolutionary era, at the peak of her powers, tells that story with style, wit, and incomparable mastery of the sources.”
--Joseph J. Ellis, author of First Family: Abigail and John Adams

Hamilton and Madison and Jay and Beeman,
The Federalist Papers,
Penguin Books; 1st edition (August 28, 2012),
ISBN 978-0143121978
Week 14: Tue., Jan. 30, 2024
George Washington
WEEK 14
George Washington (February 22, 1732 – December 14, 1799) was an American military officer, statesman, and Founding Father who served as the first president of the United States from 1789 to 1797. Appointed by the Second Continental Congress as commander of the Continental Army in June 1775, Washington led Patriot forces to victory in the American Revolutionary War and then served as president of the Constitutional Convention in 1787, which drafted and ratified the Constitution of the United States and established the American federal government. Washington has been called the "Father of his Country" for his manifold leadership in the nation's founding. Washington's first public office, from 1749 to 1750, was as surveyor of Culpeper County, Virginia. He subsequently received his first military training and was assigned command of the Virginia Regiment during the French and Indian War. He was later elected to the Colony of Virginia's House of Burgesses and was named a delegate to the Continental Congress in Philadelphia, which appointed him Commander-in-Chief of the Continental Army, the Continental Army's most senior military position. As commander of the Continental Army, Washington led American forces to a decisive victory over the British in the Revolutionary War, leading the British to sign the Treaty of Paris in 1783, which acknowledged the sovereignty and independence of the Thirteen Colonies and paved the way for the establishment of the United States. He resigned his commission in 1783 after the conclusion of the Revolutionary War. Following victory in the Revolutionary War, Washington played an indispensable role in adopting and ratifying the Constitution of the United States, which replaced the Articles of Confederation in 1789 and remains the world's longest-standing written and codified national constitution to this day. He was then twice elected president by the Electoral College unanimously. As the first U.S. president, Washington implemented a strong, well-financed national government while remaining impartial in a fierce rivalry that emerged between cabinet members Thomas Jefferson and Alexander Hamilton. During the French Revolution, he proclaimed a policy of neutrality while sanctioning the Jay Treaty. He set enduring precedents for the office of president, including use of the title "Mr. President" and taking an Oath of Office with his hand on a Bible. His Farewell Address on September 19, 1796, is a preeminent statement on republicanism in which he wrote about the importance of national unity and the dangers regionalism, partisanship, and foreign influence pose to it. Upon his death on December 14, 1799, Henry Lee eulogized Washington as "first in war, first in peace, and first in the hearts of his countrymen". He has been memorialized by monuments, a federal holiday, various media depictions, geographical locations including the national capital, the State of Washington, stamps, and currency. Many scholars and ordinary Americans alike rank him among the greatest U.S. presidents. (Wikipedia)
BEST BIOGRAPHY OF GEORGE WASHINGTON
From the Publisher: "From National Book Award winner Ron Chernow, a landmark biography of George Washington. In Washington: A Life celebrated biographer Ron Chernow provides a richly nuanced portrait of the father of our nation. With a breadth and depth matched by no other one-volume life of Washington, this crisply paced narrative carries the reader through his troubled boyhood, his precocious feats in the French and Indian War, his creation of Mount Vernon, his heroic exploits with the Continental Army, his presiding over the Constitutional Convention, and his magnificent performance as America's first president. Despite the reverence his name inspires, Washington remains a lifeless waxwork for many Americans, worthy but dull. A laconic man of granite self-control, he often arouses more respect than affection. In this groundbreaking work, based on massive research, Chernow dashes forever the stereotype of a stolid, unemotional man. A strapping six feet, Washington was a celebrated horseman, elegant dancer, and tireless hunter, with a fiercely guarded emotional life. Chernow brings to vivid life a dashing, passionate man of fiery opinions and many moods. Probing his private life, he explores his fraught relationship with his crusty mother, his youthful infatuation with the married Sally Fairfax, and his often conflicted feelings toward his adopted children and grandchildren. He also provides a lavishly detailed portrait of his marriage to Martha and his complex behavior as a slave master. At the same time, Washington is an astute and surprising portrait of a canny political genius who knew how to inspire people. Not only did Washington gather around himself the foremost figures of the age, including James Madison, Alexander Hamilton, John Adams, and Thomas Jefferson, but he also brilliantly orchestrated their actions to shape the new federal government, define the separation of powers, and establish the office of the presidency. In this unique biography, Ron Chernow takes us on a page-turning journey through all the formative events of America's founding. With a dramatic sweep worthy of its giant subject, Washington is a magisterial work from one of our most elegant storytellers."
Week 15: Tue., Feb. 6, 2024
Alexander Hamilton
WEEK 15
During the Revolution, Hamilton, while still in his early twenties, Hamilton became George Washington’s chief aide and played a heroic role in several battles, including the one that forced the surrender of General Cornwallis at Yorktown. Like the commander-in-chief, Hamilton thought "continentally," and he was so good at reading Washington's mind that the general trusted him to manage his correspondence and even to write his orders. And that was just the beginning of Hamilton's brilliant career.
BEST BIOGRAPHY OF HAMILTON
The #1 New York Times bestseller, and the inspiration for the hit Broadway musical Hamilton!
Pulitzer Prize-winning author Ron Chernow presents a landmark biography of Alexander Hamilton, the Founding Father who galvanized, inspired, scandalized, and shaped the newborn nation.
"Grand-scale biography at its best—thorough, insightful, consistently fair, and superbly written . . . A genuinely great book." —David McCullough
“A robust full-length portrait, in my view the best ever written, of the most brilliant, charismatic and dangerous founder of them all." —Joseph Ellis
Few figures in American history have been more hotly debated or more grossly misunderstood than Alexander Hamilton. Chernow’s biography gives Hamilton his due and sets the record straight, deftly illustrating that the political and economic greatness of today’s America is the result of Hamilton’s countless sacrifices to champion ideas that were often wildly disputed during his time. “To repudiate his legacy,” Chernow writes, “is, in many ways, to repudiate the modern world.” Chernow here recounts Hamilton’s turbulent life: an illegitimate, largely self-taught orphan from the Caribbean, he came out of nowhere to take America by storm, rising to become George Washington’s aide-de-camp in the Continental Army, coauthoring The Federalist Papers, founding the Bank of New York, leading the Federalist Party, and becoming the first Treasury Secretary of the United States.Historians have long told the story of America’s birth as the triumph of Jefferson’s democratic ideals over the aristocratic intentions of Hamilton. Chernow presents an entirely different man, whose legendary ambitions were motivated not merely by self-interest but by passionate patriotism and a stubborn will to build the foundations of American prosperity and power. His is a Hamilton far more human than we’ve encountered before—from his shame about his birth to his fiery aspirations, from his intimate relationships with childhood friends to his titanic feuds with Jefferson, Madison, Adams, Monroe, and Burr, and from his highly public affair with Maria Reynolds to his loving marriage to his loyal wife Eliza. And never before has there been a more vivid account of Hamilton’s famous and mysterious death in a duel with Aaron Burr in July of 1804.
Chernow’s biography is not just a portrait of Hamilton, but the story of America’s birth seen through its most central figure. At a critical time to look back to our roots, Alexander Hamilton will remind readers of the purpose of our institutions and our heritage as Americans.
Week 16: Tue., Feb. 13, 2024
Thomas Jefferson
WEEK 16
 Thomas Jefferson (1743–1826) was an American statesman, diplomat, lawyer, architect, philosopher, and Founding Father who served as the third president of the United States from 1801 to 1809.He was the primary author of the Declaration of Independence. Following the American Revolutionary War and prior to becoming president in 1801, Jefferson was the nation's first U.S. secretary of state under George Washington and then the nation's second vice president under John Adams. During the American Revolution, Jefferson represented Virginia at the Second Continental Congress and served as the second governor of Virginia from 1779 to 1781. In 1785, Congress appointed Jefferson U.S. minister to France, where he served from 1785 to 1789. President Washington then appointed Jefferson the nation's first secretary of state, where he served from 1790 to 1793. During this time, in the early 1790s, Jefferson and James Madison organized the Democratic-Republican Party to oppose the Federalist Party during the formation of the nation's First Party System. Jefferson and Federalist John Adams became both friends and political rivals. In the 1796 U.S. presidential election between the two, Jefferson came in second, which made him Adams' vice president under the electoral laws of the time. Four years later, in the 1800 presidential election, Jefferson again challenged Adams, and won the presidency. In 1804, Jefferson was reelected overwhelmingly to a second term. As president, Jefferson assertively defended the nation's shipping and trade interests against Barbary pirates and aggressive British trade policies. Beginning in 1803, he promoted a western expansionist policy with the Louisiana Purchase, which doubled the nation's geographic size. To make room for settlement, Jefferson began the process of Indian tribal removal from the newly acquired territory. As a result of peace negotiations with France, Jefferson was able to reduce military forces and expenditures. In his second presidential term, Jefferson was beset by difficulties at home, including the trial of his former vice president Aaron Burr. In 1807, American foreign trade was diminished when Jefferson implemented the Embargo Act to defend the nation's industries from British threats to U.S. shipping.
Thomas Jefferson (1743–1826) was an American statesman, diplomat, lawyer, architect, philosopher, and Founding Father who served as the third president of the United States from 1801 to 1809.He was the primary author of the Declaration of Independence. Following the American Revolutionary War and prior to becoming president in 1801, Jefferson was the nation's first U.S. secretary of state under George Washington and then the nation's second vice president under John Adams. During the American Revolution, Jefferson represented Virginia at the Second Continental Congress and served as the second governor of Virginia from 1779 to 1781. In 1785, Congress appointed Jefferson U.S. minister to France, where he served from 1785 to 1789. President Washington then appointed Jefferson the nation's first secretary of state, where he served from 1790 to 1793. During this time, in the early 1790s, Jefferson and James Madison organized the Democratic-Republican Party to oppose the Federalist Party during the formation of the nation's First Party System. Jefferson and Federalist John Adams became both friends and political rivals. In the 1796 U.S. presidential election between the two, Jefferson came in second, which made him Adams' vice president under the electoral laws of the time. Four years later, in the 1800 presidential election, Jefferson again challenged Adams, and won the presidency. In 1804, Jefferson was reelected overwhelmingly to a second term. As president, Jefferson assertively defended the nation's shipping and trade interests against Barbary pirates and aggressive British trade policies. Beginning in 1803, he promoted a western expansionist policy with the Louisiana Purchase, which doubled the nation's geographic size. To make room for settlement, Jefferson began the process of Indian tribal removal from the newly acquired territory. As a result of peace negotiations with France, Jefferson was able to reduce military forces and expenditures. In his second presidential term, Jefferson was beset by difficulties at home, including the trial of his former vice president Aaron Burr. In 1807, American foreign trade was diminished when Jefferson implemented the Embargo Act to defend the nation's industries from British threats to U.S. shipping.(Wikipedia)
RECOMMENDED READING
Week 17: Tue., Feb. 20, 2024
Louisiana Purchase
WEEK 17
 The Louisiana Purchase was the acquisition of the territory of Louisiana by the United States from the French First Republic in 1803. This consisted of most of the land in the Mississippi River's drainage basin west of the river. In return for fifteen million dollars, or approximately eighteen dollars per square mile, the United States nominally acquired a total of 828,000 sq mi in Middle America. However, France only controlled a small fraction of this area, most of which was inhabited by Native Americans; effectively, for the majority of the area, the United States bought the preemptive right to obtain Indian lands by treaty or by conquest, to the exclusion of other colonial powers. The Kingdom of France had controlled the Louisiana territory from 1682 until it was ceded to Spain in 1762. In 1800, Napoleon, the First Consul of the French Republic, regained ownership of Louisiana in exchange for Tuscany as part of a broader effort to re-establish a French colonial empire in North America. However, France's failure to suppress a revolt in Saint-Domingue, coupled with the prospect of renewed warfare with the United Kingdom, prompted Napoleon to consider selling Louisiana to the United States. Acquisition of Louisiana was a long-term goal of President Thomas Jefferson, who was especially eager to gain control of the crucial Mississippi River port of New Orleans. Jefferson tasked James Monroe and Robert R. Livingston with purchasing New Orleans. Negotiating with French Treasury Minister François Barbé-Marbois, the U.S. representatives quickly agreed to purchase the entire territory of Louisiana after it was offered. Overcoming the opposition of the Federalist Party, Jefferson and Secretary of State James Madison persuaded Congress to ratify and fund the Louisiana Purchase.(Wikipedia)
The Louisiana Purchase was the acquisition of the territory of Louisiana by the United States from the French First Republic in 1803. This consisted of most of the land in the Mississippi River's drainage basin west of the river. In return for fifteen million dollars, or approximately eighteen dollars per square mile, the United States nominally acquired a total of 828,000 sq mi in Middle America. However, France only controlled a small fraction of this area, most of which was inhabited by Native Americans; effectively, for the majority of the area, the United States bought the preemptive right to obtain Indian lands by treaty or by conquest, to the exclusion of other colonial powers. The Kingdom of France had controlled the Louisiana territory from 1682 until it was ceded to Spain in 1762. In 1800, Napoleon, the First Consul of the French Republic, regained ownership of Louisiana in exchange for Tuscany as part of a broader effort to re-establish a French colonial empire in North America. However, France's failure to suppress a revolt in Saint-Domingue, coupled with the prospect of renewed warfare with the United Kingdom, prompted Napoleon to consider selling Louisiana to the United States. Acquisition of Louisiana was a long-term goal of President Thomas Jefferson, who was especially eager to gain control of the crucial Mississippi River port of New Orleans. Jefferson tasked James Monroe and Robert R. Livingston with purchasing New Orleans. Negotiating with French Treasury Minister François Barbé-Marbois, the U.S. representatives quickly agreed to purchase the entire territory of Louisiana after it was offered. Overcoming the opposition of the Federalist Party, Jefferson and Secretary of State James Madison persuaded Congress to ratify and fund the Louisiana Purchase.(Wikipedia)
Week 18: Tue., Feb. 27, 2024
James Madison
WEEK 18
 James Madison (1751–1836) was an American statesman, diplomat, and Founding Father who served as the fourth president of the United States from 1809 to 1817. Madison was popularly acclaimed the "Father of the Constitution" for his pivotal role in drafting and promoting the Constitution of the United States and the Bill of Rights. Madison was born into a prominent slave-owning planter family in Virginia. He served as a member of the Virginia House of Delegates and the Continental Congress during and after the American Revolutionary War. Dissatisfied with the weak national government established by the Articles of Confederation, he helped organize the Constitutional Convention, which produced a new constitution designed to strengthen republican government against democratic assembly. Madison's Virginia Plan was the basis for the convention's deliberations, and he was an influential voice at the convention. He became one of the leaders in the movement to ratify the Constitution and joined Alexander Hamilton and John Jay in writing The Federalist Papers, a series of pro-ratification essays that remains prominent among works of political science in American history. Madison emerged as an important leader in the House of Representatives and was a close adviser to President George Washington. During the early 1790s, Madison opposed the economic program and the accompanying centralization of power favored by Secretary of the Treasury Hamilton. Alongside Thomas Jefferson, he organized the Democratic–Republican Party in opposition to Hamilton's Federalist Party. After Jefferson was elected president in 1800, Madison served as his Secretary of State from 1801 to 1809 and supported Jefferson in the case of Marbury v. Madison. While Madison was Secretary of State, Jefferson made the Louisiana Purchase, and later, as President, Madison oversaw related disputes in the Northwest Territories. Madison was elected president in 1808. Motivated by desire to acquire land held by Britain, Spain, and Native Americans, and after diplomatic protests with a trade embargo failed to end British seizures of American shipped goods, Madison led the United States into the War of 1812. Although the war ended inconclusively, many Americans viewed the war's outcome as a successful "second war of independence" against Britain. Madison was re-elected in 1812, albeit by a smaller margin. The war convinced Madison of the necessity of a stronger federal government. He presided over the creation of the Second Bank of the United States and the enactment of the protective Tariff of 1816. By treaty or through war, Native American tribes ceded 26,000,000 acres (11,000,000 ha) of land to the United States under Madison's presidency. Retiring from public office at the end of his presidency in 1817, Madison returned to his plantation, Montpelier, and died there in 1836. During his lifetime, Madison was a slave owner. In 1783, to prevent a slave rebellion at Montpelier, Madison freed one of his slaves. He did not free any slaves in his will. Among historians, Madison is considered one of the most important Founding Fathers of the United States. Leading historians have generally ranked him as an above-average president, although they are critical of his endorsement of slavery and his leadership during the War of 1812. Madison's name is commemorated in many landmarks across the nation, both publicly and privately, with prominent examples including Madison Square Garden, James Madison University, the James Madison Memorial Building, and the USS James Madison.(Wikipedia)
James Madison (1751–1836) was an American statesman, diplomat, and Founding Father who served as the fourth president of the United States from 1809 to 1817. Madison was popularly acclaimed the "Father of the Constitution" for his pivotal role in drafting and promoting the Constitution of the United States and the Bill of Rights. Madison was born into a prominent slave-owning planter family in Virginia. He served as a member of the Virginia House of Delegates and the Continental Congress during and after the American Revolutionary War. Dissatisfied with the weak national government established by the Articles of Confederation, he helped organize the Constitutional Convention, which produced a new constitution designed to strengthen republican government against democratic assembly. Madison's Virginia Plan was the basis for the convention's deliberations, and he was an influential voice at the convention. He became one of the leaders in the movement to ratify the Constitution and joined Alexander Hamilton and John Jay in writing The Federalist Papers, a series of pro-ratification essays that remains prominent among works of political science in American history. Madison emerged as an important leader in the House of Representatives and was a close adviser to President George Washington. During the early 1790s, Madison opposed the economic program and the accompanying centralization of power favored by Secretary of the Treasury Hamilton. Alongside Thomas Jefferson, he organized the Democratic–Republican Party in opposition to Hamilton's Federalist Party. After Jefferson was elected president in 1800, Madison served as his Secretary of State from 1801 to 1809 and supported Jefferson in the case of Marbury v. Madison. While Madison was Secretary of State, Jefferson made the Louisiana Purchase, and later, as President, Madison oversaw related disputes in the Northwest Territories. Madison was elected president in 1808. Motivated by desire to acquire land held by Britain, Spain, and Native Americans, and after diplomatic protests with a trade embargo failed to end British seizures of American shipped goods, Madison led the United States into the War of 1812. Although the war ended inconclusively, many Americans viewed the war's outcome as a successful "second war of independence" against Britain. Madison was re-elected in 1812, albeit by a smaller margin. The war convinced Madison of the necessity of a stronger federal government. He presided over the creation of the Second Bank of the United States and the enactment of the protective Tariff of 1816. By treaty or through war, Native American tribes ceded 26,000,000 acres (11,000,000 ha) of land to the United States under Madison's presidency. Retiring from public office at the end of his presidency in 1817, Madison returned to his plantation, Montpelier, and died there in 1836. During his lifetime, Madison was a slave owner. In 1783, to prevent a slave rebellion at Montpelier, Madison freed one of his slaves. He did not free any slaves in his will. Among historians, Madison is considered one of the most important Founding Fathers of the United States. Leading historians have generally ranked him as an above-average president, although they are critical of his endorsement of slavery and his leadership during the War of 1812. Madison's name is commemorated in many landmarks across the nation, both publicly and privately, with prominent examples including Madison Square Garden, James Madison University, the James Madison Memorial Building, and the USS James Madison.(Wikipedia)
Week 19: Tue., Mar. 5, 2024
James Monroe
WEEK 19
 James Monroe (1758–July 4, 1831) was an American statesman, lawyer, diplomat, and Founding Father who served as the fifth president of the United States from 1817 to 1825, a member of the Democratic-Republican Party. He was the last Founding Father to serve as president as well as the last president of the Virginia dynasty and the Republican Generation. His presidency coincided with the Era of Good Feelings, concluding the First Party System era of American politics. He is best known for issuing the Monroe Doctrine, a policy of limiting European colonialism in the Americas. Previously he served as governor of Virginia, a member of the United States Senate, U.S. ambassador to France and Britain, the seventh secretary of state, and the eighth secretary of war. Monroe served in the Continental Army during the American Revolutionary War. He studied law under Thomas Jefferson from 1780 to 1783 and served as a delegate in the Continental Congress as well as a delegate to the Virginia Ratifying Convention. He opposed the ratification of the United States Constitution. In 1790, he won election to the Senate where he became a leader of the Democratic-Republican Party. He left the Senate in 1794 to serve as President George Washington's ambassador to France but was recalled by Washington in 1796. Monroe won the election as Governor of Virginia in 1799 and strongly supported Jefferson's candidacy in the 1800 presidential election. As President Jefferson's special envoy, Monroe helped negotiate the Louisiana Purchase, through which the United States nearly doubled in size. Monroe fell out with his longtime friend James Madison after Madison rejected the Monroe–Pinkney Treaty that Monroe negotiated with Britain. He unsuccessfully challenged Madison for the Democratic-Republican nomination in the 1808 presidential election, but he joined Madison's administration as Secretary of State in 1811. During the later stages of the War of 1812, Monroe simultaneously served as Madison's Secretary of State and Secretary of War. Monroe's wartime leadership established him as Madison's heir apparent, and he easily defeated Federalist candidate Rufus King in the 1816 presidential election. During Monroe's tenure as president, the Federalist Party collapsed as a national political force and Monroe was re-elected, virtually unopposed, in 1820. As president, Monroe signed the Missouri Compromise, which admitted Missouri as a slave state and banned slavery from territories north of the 36°30′ parallel. In foreign affairs, Monroe and Secretary of State John Quincy Adams favored a policy of conciliation with Britain and a policy of expansionism against the Spanish Empire. In the 1819 Adams–Onís Treaty with Spain, the United States secured Florida and established its western border with New Spain. In 1823, Monroe announced the United States' opposition to any European intervention in the recently independent countries of the Americas with the Monroe Doctrine, which became a landmark in American foreign policy. Monroe was a member of the American Colonization Society which supported the colonization of Africa by freed slaves, and Liberia's capital of Monrovia is named in his honor. Following his retirement in 1825, Monroe was plagued by financial difficulties and died on July 4, 1831, in New York City—sharing a distinction with Presidents John Adams and Thomas Jefferson of dying on the anniversary of U.S. independence. (Wikipedia)
James Monroe (1758–July 4, 1831) was an American statesman, lawyer, diplomat, and Founding Father who served as the fifth president of the United States from 1817 to 1825, a member of the Democratic-Republican Party. He was the last Founding Father to serve as president as well as the last president of the Virginia dynasty and the Republican Generation. His presidency coincided with the Era of Good Feelings, concluding the First Party System era of American politics. He is best known for issuing the Monroe Doctrine, a policy of limiting European colonialism in the Americas. Previously he served as governor of Virginia, a member of the United States Senate, U.S. ambassador to France and Britain, the seventh secretary of state, and the eighth secretary of war. Monroe served in the Continental Army during the American Revolutionary War. He studied law under Thomas Jefferson from 1780 to 1783 and served as a delegate in the Continental Congress as well as a delegate to the Virginia Ratifying Convention. He opposed the ratification of the United States Constitution. In 1790, he won election to the Senate where he became a leader of the Democratic-Republican Party. He left the Senate in 1794 to serve as President George Washington's ambassador to France but was recalled by Washington in 1796. Monroe won the election as Governor of Virginia in 1799 and strongly supported Jefferson's candidacy in the 1800 presidential election. As President Jefferson's special envoy, Monroe helped negotiate the Louisiana Purchase, through which the United States nearly doubled in size. Monroe fell out with his longtime friend James Madison after Madison rejected the Monroe–Pinkney Treaty that Monroe negotiated with Britain. He unsuccessfully challenged Madison for the Democratic-Republican nomination in the 1808 presidential election, but he joined Madison's administration as Secretary of State in 1811. During the later stages of the War of 1812, Monroe simultaneously served as Madison's Secretary of State and Secretary of War. Monroe's wartime leadership established him as Madison's heir apparent, and he easily defeated Federalist candidate Rufus King in the 1816 presidential election. During Monroe's tenure as president, the Federalist Party collapsed as a national political force and Monroe was re-elected, virtually unopposed, in 1820. As president, Monroe signed the Missouri Compromise, which admitted Missouri as a slave state and banned slavery from territories north of the 36°30′ parallel. In foreign affairs, Monroe and Secretary of State John Quincy Adams favored a policy of conciliation with Britain and a policy of expansionism against the Spanish Empire. In the 1819 Adams–Onís Treaty with Spain, the United States secured Florida and established its western border with New Spain. In 1823, Monroe announced the United States' opposition to any European intervention in the recently independent countries of the Americas with the Monroe Doctrine, which became a landmark in American foreign policy. Monroe was a member of the American Colonization Society which supported the colonization of Africa by freed slaves, and Liberia's capital of Monrovia is named in his honor. Following his retirement in 1825, Monroe was plagued by financial difficulties and died on July 4, 1831, in New York City—sharing a distinction with Presidents John Adams and Thomas Jefferson of dying on the anniversary of U.S. independence. (Wikipedia)
RECOMMENDED READING
Week 20: Tue., Mar. 12, 2024
John Quincy Adams
WEEK 20
RECOMMENDED READING

James Traub,
John Quincy Adams: Militant Spirit,
Basic Books; Reprint edition (October 10, 2017),
ISBN 978-0465093830





